Dataframes¶
marimo makes you more productive when working with dataframes, the most common Python tool for interacting with data.
Display dataframes in a rich, interactive table and chart views
Select data from tables or charts and get selections back as dataframes
Transform dataframes with filters, groupbys, aggregations, and more, no code required
marimo integrates with Pandas and Polars dataframes natively. The examples on this page use Pandas, but Polars works too.
Displaying dataframes¶
You can display dataframes directly in the output area of a cell, by including them in the last expression of the cell:
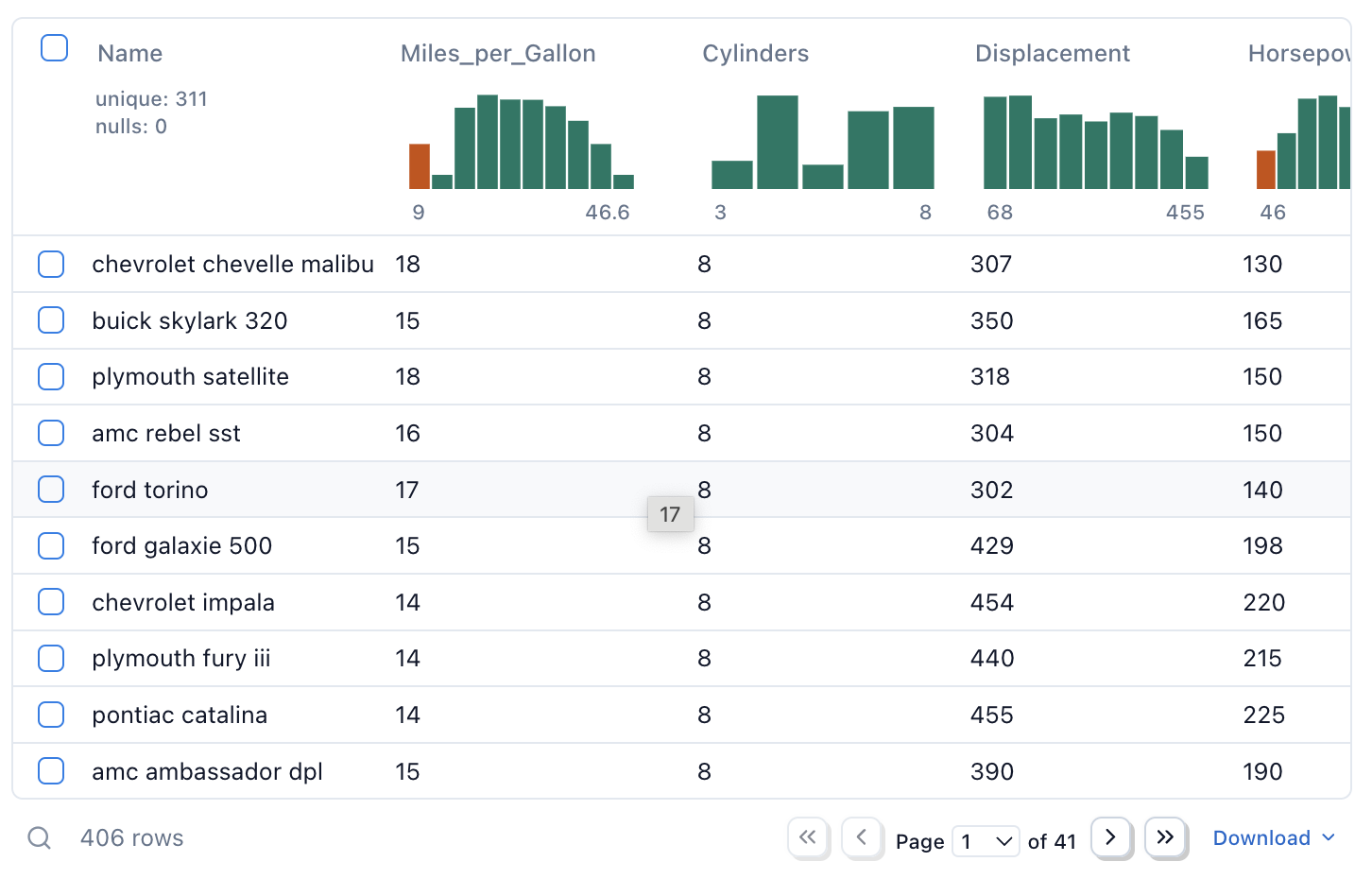
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_json(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vega/vega-datasets/master/data/cars.json"
)
df
By default the dataframe is displayed using mo.ui.table, which provides a
a rich, interactive table view. You can also use mo.plain to revert to the
to the default HTML representation.
df = pd.read_json(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vega/vega-datasets/master/data/cars.json"
)
mo.plain(df)
Rich displays.
You can display dataframes in rich tables or charts using the
mo.ui.table or mo.ui.altair_chart
elements.
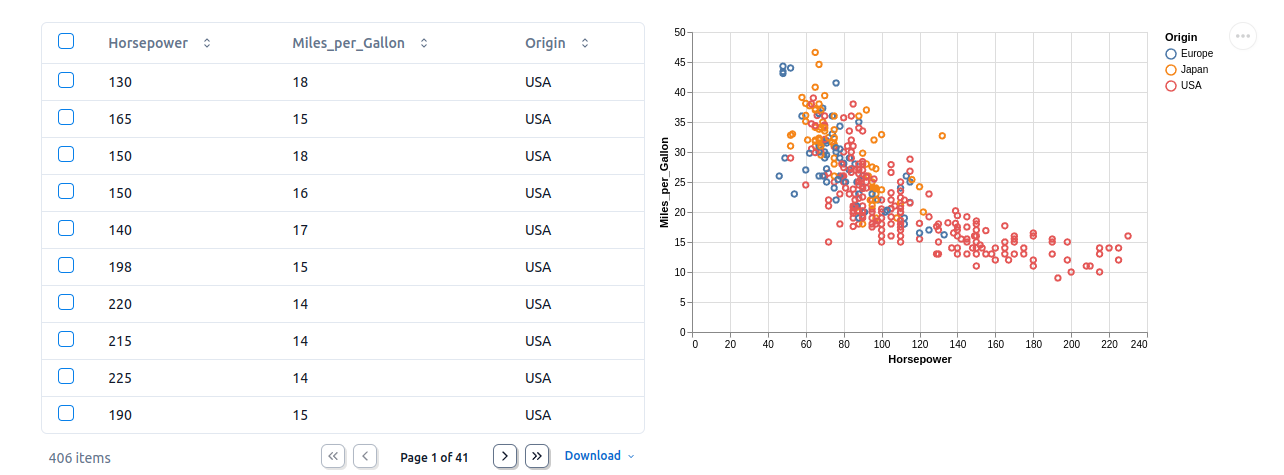
import marimo as mo
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_json(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vega/vega-datasets/master/data/cars.json"
)[["Horsepower", "Miles_per_Gallon", "Origin"]]
mo.hstack(
[
mo.ui.table(df),
mo.ui.altair_chart(
alt.Chart(df)
.mark_point()
.encode(x="Horsepower", y="Miles_per_Gallon", color="Origin")
),
],
widths="equal",
)
Selecting dataframes¶
Select data in a table or Plotly/Altair plot, and your selection is automatically sent to Python as a Pandas dataframe.
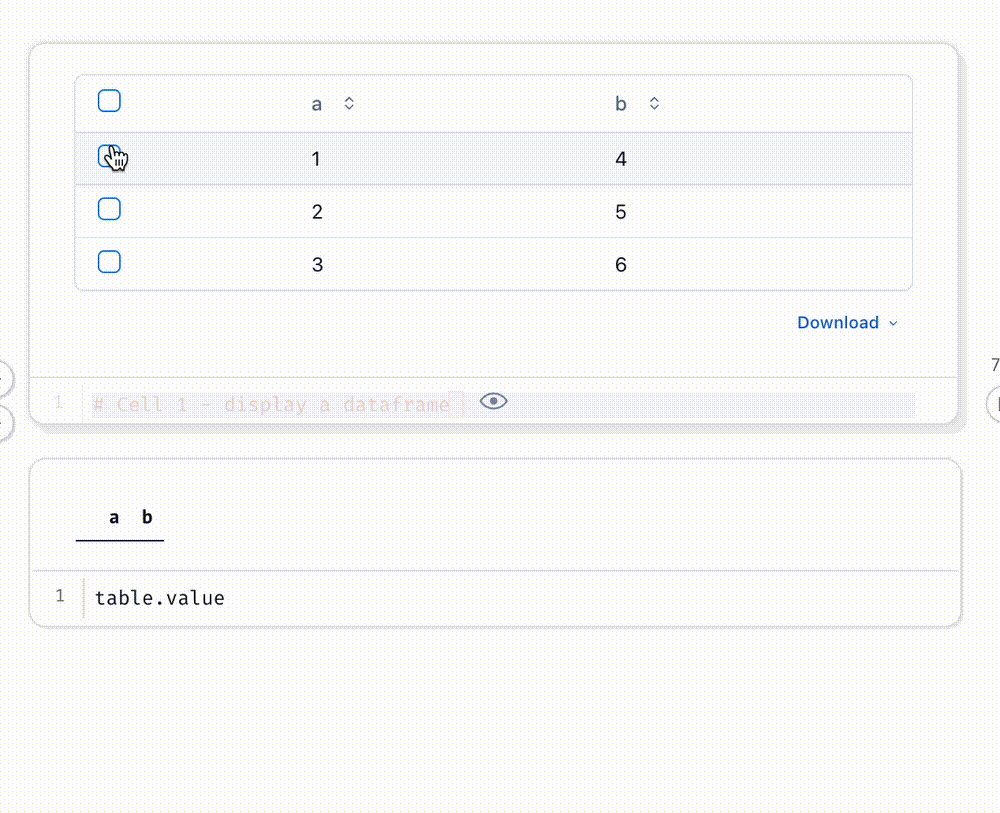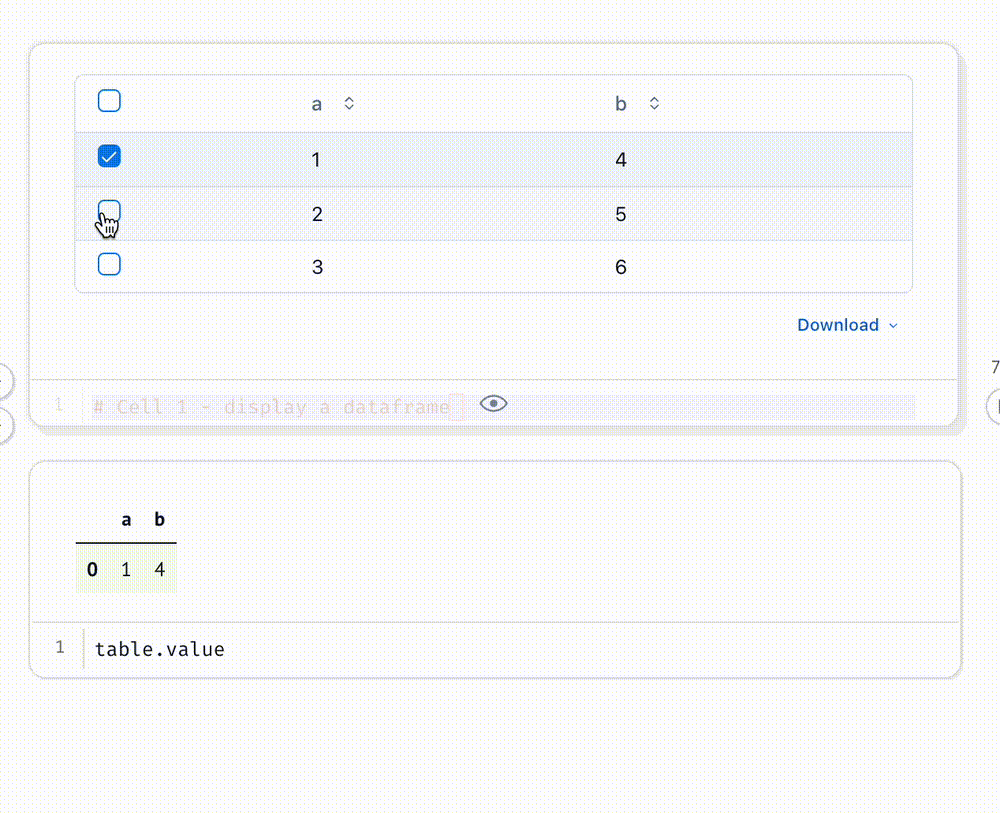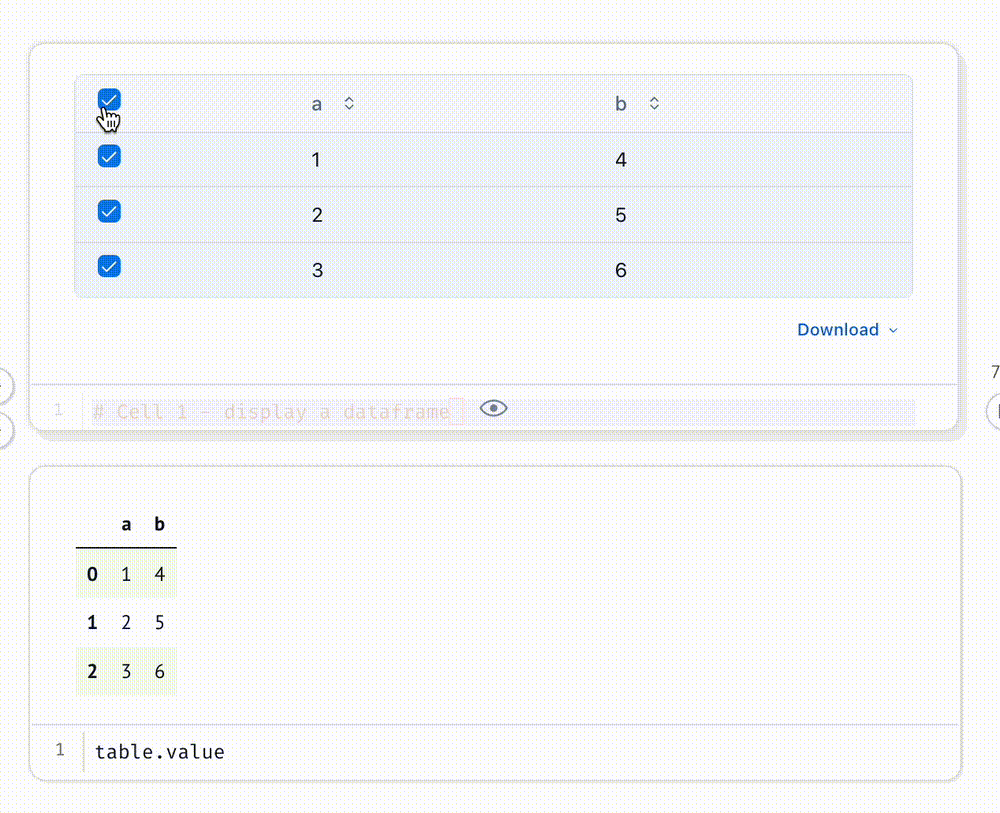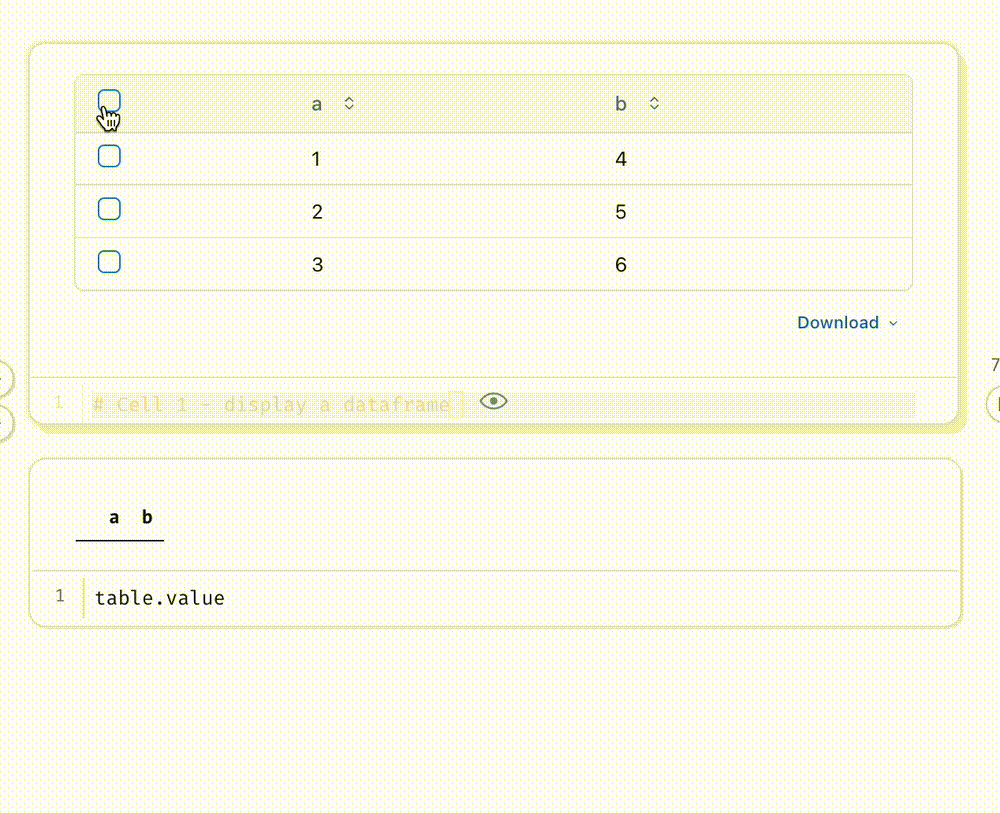
# Cell 1 - display a dataframe
import marimo as mo
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({"a": [1, 2, 3], "b": [4, 5, 6]})
table = mo.ui.table(df, selection="multi")
table
# Cell 2 - display the selection
table.value
Transforming dataframes¶
No-code transformations¶
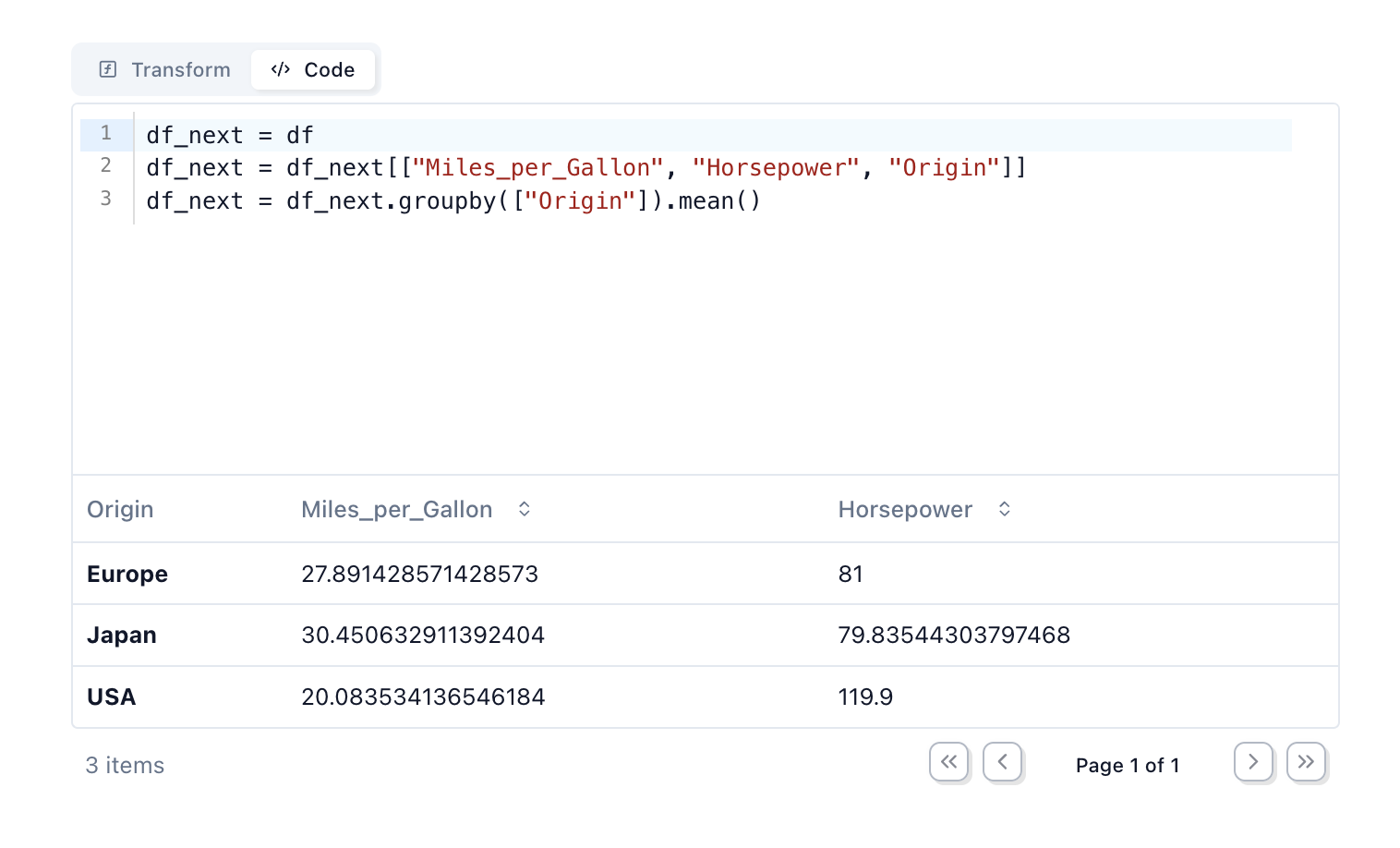
Use mo.ui.dataframe to interactively
transform a dataframe with a GUI, no coding required!. When you’re done, you
can copy the code that the GUI generated for you and paste it into your
notebook.
# Cell 1
import marimo as mo
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({"person": ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"], "age": [20, 30, 40]})
transformed_df = mo.ui.dataframe(df)
transformed_df
# Cell 2
# transformed_df.value holds the transformed dataframe
transformed_df.value
Custom filters¶
Create custom filters with marimo UI elements, like sliders and dropdowns.
# Cell 1 - create a dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"person": ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"], "age": [20, 30, 40]})
# Cell 2 - create a filter
age_filter = mo.ui.slider(start=0, stop=100, value=50, label="Max age")
age_filter
# Cell 3 - display the transformed dataframe
filtered_df = df[df["age"] < age_filter.value]
mo.ui.table(filtered_df)
Polars support¶
marimo provides first-class support for Polars, a modern, high-performance alternative to Pandas. You can use Polars dataframes seamlessly with marimo’s interactive features, just like you would with Pandas.
Displaying Polars dataframes¶
Polars dataframes can be displayed directly in marimo cells:
import polars as pl
df = pl.DataFrame({
"A": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
"B": ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"],
"C": [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5]
})
df
This will render an interactive rich table view of the Polars dataframe.
Rich visualizations¶
You can use mo.ui.table or mo.ui.altair_chart for displaying Polars dataframes getting
the row selections or points on a chart back as a Polars dataframe.
import marimo as mo
import polars as pl
import altair as alt
df = pl.DataFrame({
"category": ["A", "B", "C", "D"],
"value": [10, 20, 15, 25]
})
chart = mo.ui.altair_chart(
alt.Chart(df).mark_bar().encode(
x="category",
y="value"
)
)
chart
# Cell 2
# chart.value holds the selected data as a Polars dataframe
chart.value
Interactive transformations¶
Use mo.ui.dataframe to interactively transform Polars dataframes:
import marimo as mo
import polars as pl
df = pl.DataFrame({
"name": ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David"],
"age": [25, 30, 35, 40],
"city": ["New York", "London", "Paris", "Tokyo"]
})
transformed_df = mo.ui.dataframe(df)
transformed_df
# Cell 2
# transformed_df.value holds the transformed dataframe
transformed_df.value
Filters for Polars dataframes¶
Create custom filters for Polars dataframes using marimo UI elements:
import marimo as mo
import polars as pl
df = pl.DataFrame({
"name": ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David"],
"age": [25, 30, 35, 40],
"city": ["New York", "London", "Paris", "Tokyo"]
})
age_filter = mo.ui.slider.from_series(df["age"], label="Max age")
city_filter = mo.ui.dropdown.from_series(df["city"], label="City")
mo.hstack([age_filter, city_filter])
# Cell 2
filtered_df = df.filter((pl.col("age") <= age_filter.value) & (pl.col("city") == city_filter.value))
mo.ui.table(filtered_df)
Example notebook¶
For a comprehensive example of using Polars with marimo, check out our Polars example notebook.
You can run it yourself with:
marimo edit https://raw.githubusercontent.com/marimo-team/marimo/main/examples/third_party/polars/polars_example.py